The IBM Storage Scale System 6000 has been introduced as an upgraded appliance with twice the throughput capability compared to its predecessor, the ESS 3500.
This system leverages IBM's renowned parallel file system software, formerly known as GPFS, which has established popularity in high-performance computing (HPC) and related environments.
The ESS series integrates scale-up and scale-out capabilities, supporting up to 1,000 appliances, all equipped with IBM's Storage Scale software.
Each node in the current ESS 3500 features 24-slot 2U form factors with dual active controllers, NVMe SSDs or IBM's proprietary Flash Core Modules (FCMs), and high-speed connectivity options such as 100 Gbit Ethernet or 200 Gbit HDR InfiniBand ports, delivering up to 126 GB/sec throughputs per node.
According to Denis Kennelly, IBM's Storage General Manager, the Storage Scale System 6000 unifies data from core, edge, and cloud environments onto a single platform optimized for GPU-intensive workloads.
He emphasized the importance of integrating diverse data sources in near real-time, eliminating redundant data copies and continuous data ingestion cycles.
Kennelly envisions the Storage Scale System 6000 as pivotal in streamlining the information supply chain, consolidating workloads, and facilitating efficient AI training and inferencing on GPU servers.
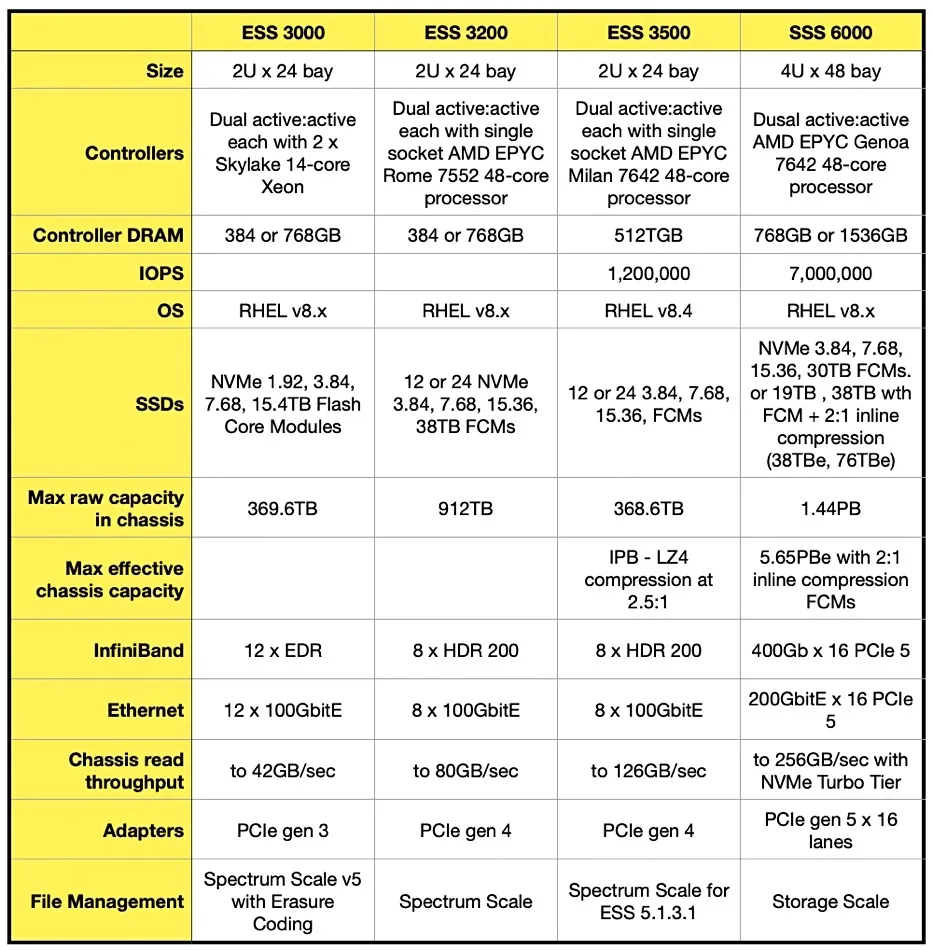
IBM has upgraded its ESS appliance lineup with the introduction of the Storage Scale System 6000, featuring significant enhancements over its predecessor, the ESS 3500. The new model boasts a larger chassis size, moving from a 24-slot 2RU configuration to a 48-slot 4RU design. It doubles the maximum capacity of raw NAND drives to 30 TB and plans to introduce inline compressing Flash Core Modules (FCMs) offering effective capacities of either 38 TB or 76 TB at a 2:1 compression ratio.
- PCIe Gen 5 Bus: The Storage Scale System 6000 operates on the PCIe Gen 5 bus, doubling the speed of the ESS 3500's PCIe Gen 4 interconnect.
- Enhanced Connectivity: Supports faster connectivity options, including 400 Gb InfiniBand (versus 200 Gb InfiniBand in the ESS 3500) and 200 GbitE (versus 100 GbitE in the predecessor).
- Upgraded Performance: Features upgraded CPUs and increased controller DRAM, elevating the maximum per-chassis data transfer rate from 126 GBps to 256 GBps.
- NVMe Turbo Tier: Includes an NVMe turbo tier for enhanced speed in transferring small files.
- GPUDirect Support: Like its predecessor, the 6000 supports Nvidia's GPUDirect protocol, enabling rapid data delivery to Nvidia GPUs by bypassing the CPU.
According to IBM, the Storage Scale System 6000 outperforms market-leading competitors by 2.5 times, although specific competitors were not named. Current suppliers supporting Nvidia's GPUDirect include Dell (PowerScale), DDN, Huawei, NetApp, Pure Storage, and WekaIO.
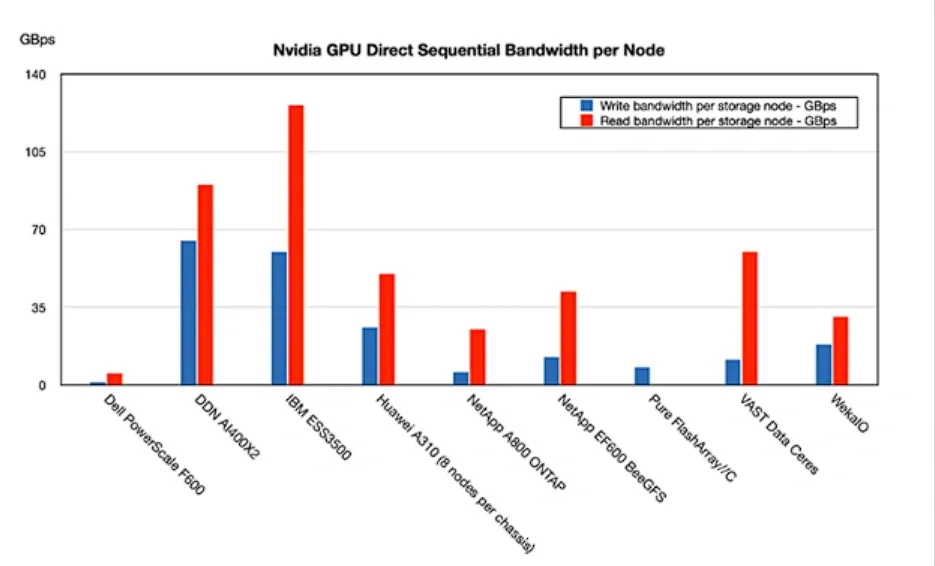
We anticipate that GPUDirect testing will demonstrate the Storage Scale System 6000 (SSS 6000) as the highest-performing system in GPUDirect data supply on a per-node basis.
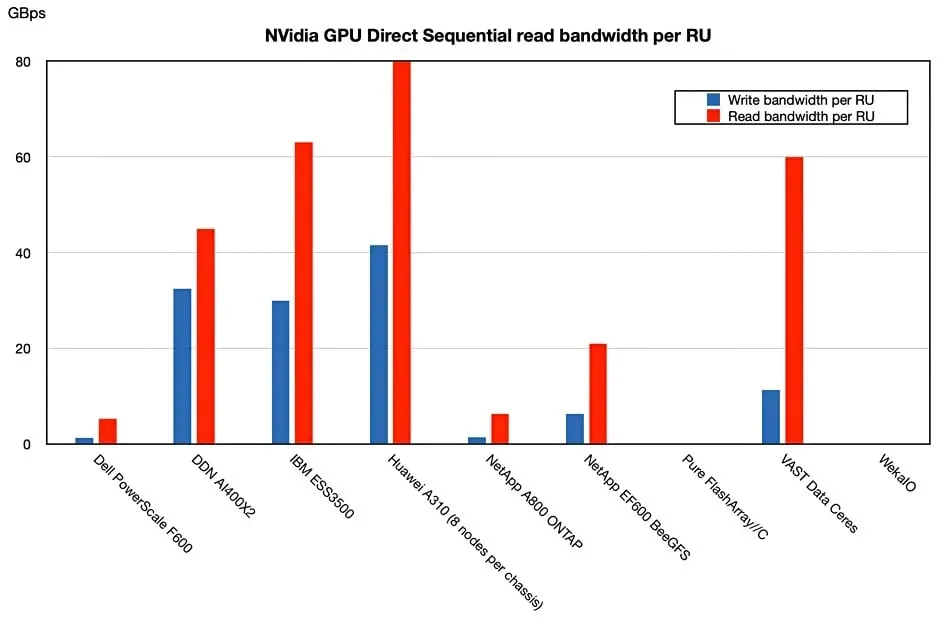
However, it falls short of Huawei's A310 in per-RU performance, with an estimated 64 GBps read bandwidth compared to the A310's superior 80 GBps.
IBM's Storage Scale System 6000 will receive new NVMe Flash Core Modules (FCMs) utilizing QLC (4bits/cell) NAND technology in the first half of 2024.
- Cost Efficiency: The new FCMs are expected to offer a 70% reduction in cost compared to the current 15.36 TB flash drives used in the ESS 3500.
- Energy Savings: These FCMs will consume 53% less energy per terabyte than the existing flash drives.
- Increased Data Density: The 6000 system will store 2.5 times more data within the same floor space as its predecessor.
- High-Capacity Configuration: Configurations using the upcoming 38 TB FCM drives with up to 2:1 inline compression are projected to achieve 900 TB per rack unit.
- Comparison to Previous Generation: The previous generation ESS 3500 with 30 TB flash drives yielded 360 TB per rack unit.
In addition to unveiling these new hardware capabilities, IBM emphasized that the Storage Scale System 6000 can function as a central hub for aggregating data from diverse sources, illustrated in a diagram depicting its role as a global data platform.
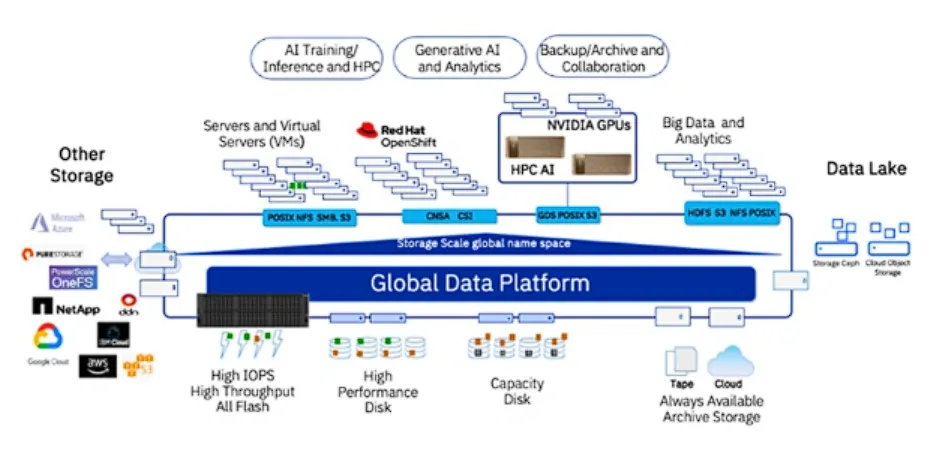
This capability includes aggregating data from external arrays like Dell PowerScale, NetApp, and Pure Storage, as well as from cloud environments. Moreover, the Storage Scale System 6000 can distribute data to tape systems or the cloud for long-term storage purposes.







